
However, now the oxygen diffuses from the alveoli, across the capillaries, and into the de-oxygenated RBC. It again arrives at thin-walled capillaries where gas exchange occurs with adjacent alveoli. It will travel through the right side of the heart and eventually is conducted through the pulmonary arterial system.
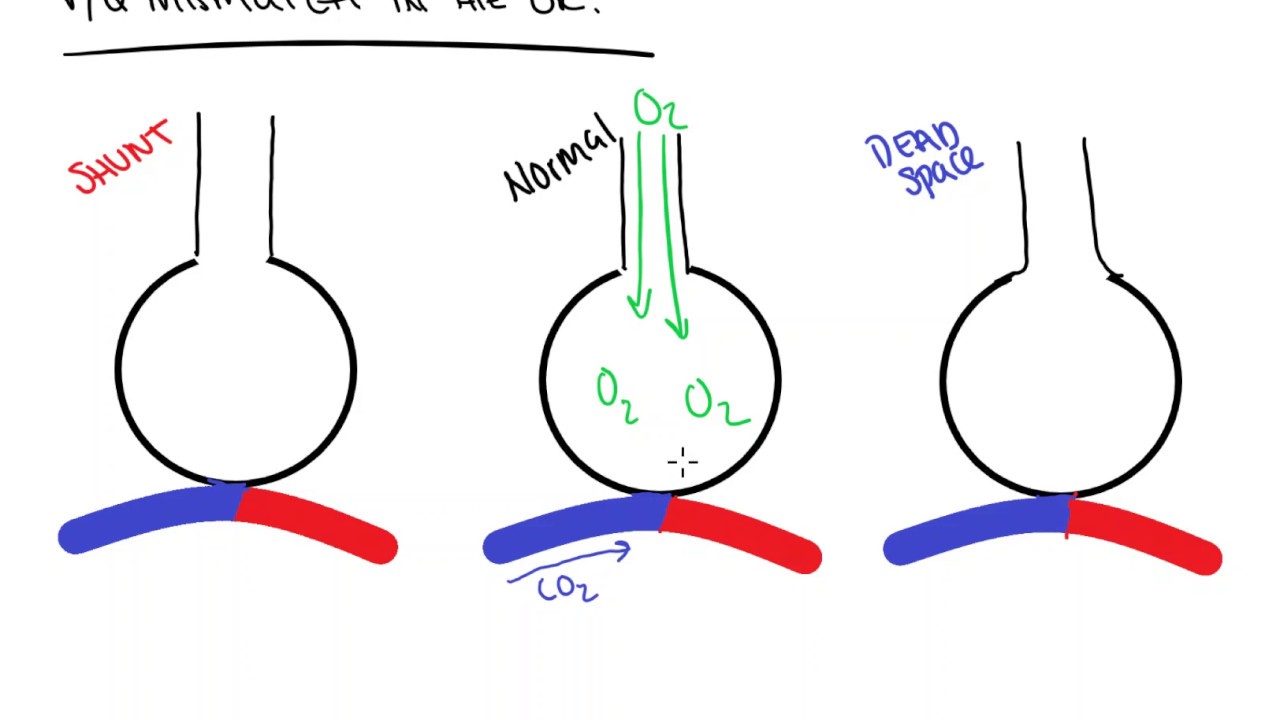
The RBC, now deoxygenated, will continue to be pushed through the body and return to the heart via the venous system. There it will serve a vital role in cellular respiration. In peripheral tissues, oxygen will leave the RBC, transverse the capillary wall, and be taken up by a cell. The capillaries are thin-walled, allowing for gasses to diffuse across their membranes. From there, the cell will travel to the capillary beds of peripheral tissues, be it the kidney, liver, muscle, skin, brain, or any other tissue that receives blood. The heart contracts pushing the cell through the aorta and into the body's arterial system. At this point in the circuit, the RBC is highly oxygenated after traversing through the pulmonary capillaries.

Let us imagine a single red blood cell as it travels through the body. The heart serves as the body's pumping system, pushing oxygen-rich blood to peripheral tissues and pulling oxygen-poor blood back toward the heart.

To understand the A-a gradient, it is first important to understand the interplay between the vascular system and the lungs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
